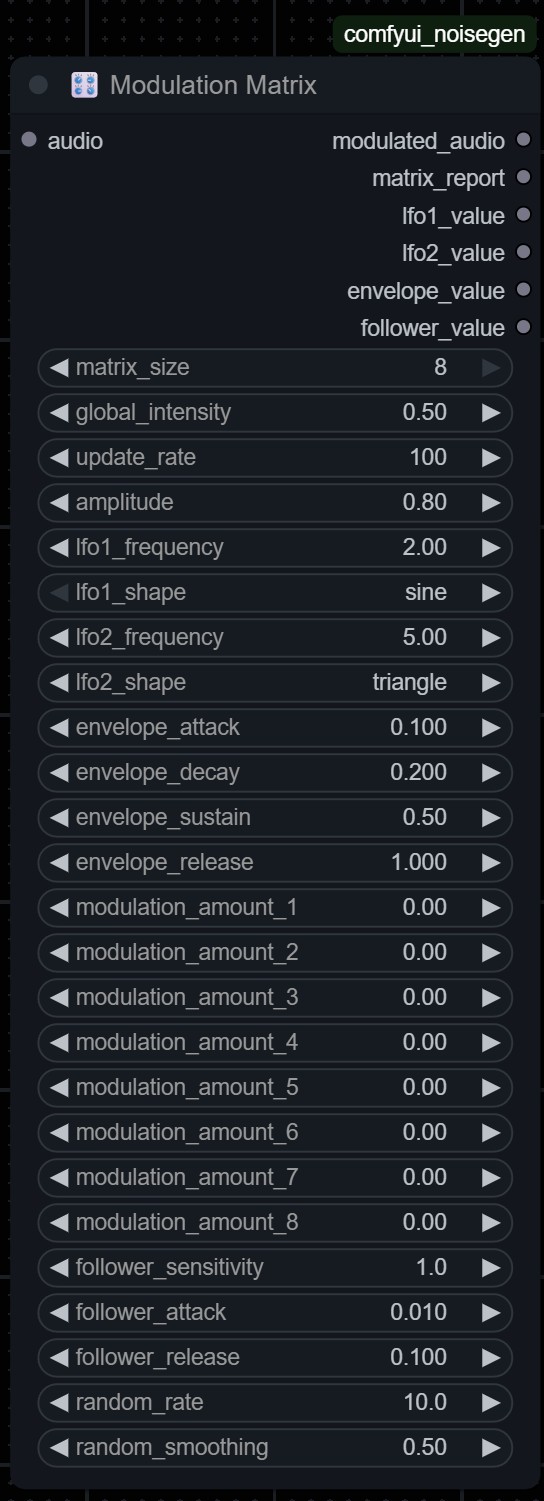
MATRIX SIZE
8 Sources × 8 Destinations
MODULATION SOURCES
LFO, Envelope, Chaos, Audio
ROUTING MODES
12 connection types
CONTROL RANGE
±100% bipolar modulation
UPDATE RATE
Audio rate (96kHz max)
PRECISION
32-bit floating point